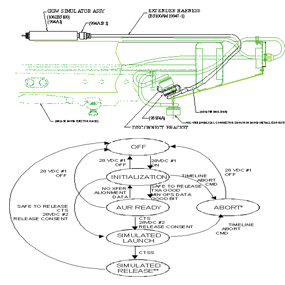
Airborne GPS-Guided Weapon Simulator (AGS)
The Airborne GPS-Guided Weapon Simulator (AGS) is fully flight-qualified unit for simulation of GPS-based MIL-1760 weapons such as JDAM, GBU-24, and WCMD. The small, lightweight AGS is intended for mounting directly on the launch platform's weapons rail or attaching to a standard bomb rack (with an optional adapter), making use of the standard MIL-1760 interface connector for its power and interface requirements. No modifications or special conditions are required in the platform's operational software, as the AGS operates as a standalone simulation of the desired GPS-Guided Weapon (GGW). This allows the AGS to be used as both a software development tool for integration of new GGW units on a platform, as well as an ideal training device. The AGS software is designed for MLV field updates, allowing for additional weapon types to be implemented quickly and easily. Originally developed for the Navy's F-14 fighter aircraft, the AGS has meet all the required environmental and operational specifications for Navy fleet use, including temperature, altitude, EMI/EMC, and aircraft carrier suitability. The AGS unit is fully programmable to provide a complete simulation of the selected weapon's interface, as well as to allow for growth in simulation of a new or modified GGWs.
The dimensions of the AGS are 10-1/2" long (including switch and connector), 6-1/2" wide, and 2" tall. The weight is approximately 1.7 lbs. Depending on installation constraints, the AGS circuitry can be repackaged to meet even smaller dimensions. The AGS incorporates a TMS320 Digital Signal Processor, in conjunction with an ILC-DDC 'ACE' 1553 interface chip, to simulate the desired GGW. Power is derived from the MIL-1760 interface's +28 VDC No. 1 input, being DC-DC converted to +5 VDC for use within the AGS. The weapon type is selected via an external six-position rotary switch. In the F-14 installation, the AGS is mounted directly to the top of the Weapons Rail on any one of the four 'belly' stations. For more conventional installations such as the F-117, the AGS can be attached to an optional bomb rack adapter. The AGS connects to the 1760 interface connector via the AGS Extender Harness that allows for flexibility in mounting position, as well as conversion of the 1760 signals to the layout of the AGS' interface connector.
For applications with security concerns, the AGS addresses this by using volatile memory only for all operational use; non-volatile memory can only be written to with connection of external ground equipment. Additionally, the AGS is designed to operate with or without batteries. Batteries are required to complete the simulation of a weapon release after Power Change-Over (PCO), allowing the final pre-launch communications and the weapon's 'interlock' signal to be opened after the +28 VDC power input is disabled by the launch platform. After completing the release simulation, the AGS disables its battery power and remains off until the launch platform re-initializes it with the +28 VDC power input. In the event security issues prevent the use of internal batteries, the AGS still provides a full simulation of the GGW interface, including the launch sequence, up until the +28 VDC No. 1 power is removed at PCO.
Modification of the AGS functionality is extremely easy through modification of the TMS320C32 DSP software. Field updates can be implemented using the AGS' MLV functionality to upload new software via the unit's 1553 interface. Variations of the GGW simulations can be implemented for special weapon interface requirements, error simulation, software validation testing and unique training scenarios. In fact, the AGS is capable of being re-programmed to simulate any 1553 device or line-replaceable unit (LRU) for in-flight simulation. As a fully flight qualified unit, the AGS allows weapon system integrators to quickly and easily simulate the function of new LRUs under development in flight, expediting the software integration process dramatically by eliminating the need to wait for actual LRU before flight testing software. The small size and weight of the AGS, coupled with its ability to be mounted on the inside or outside of the aircraft, make it an ideal general-purpose 1553 airborne LRU simulator.